
General Router FAQ
Router DNS Operation

|
General Router FAQRouter DNS Operation |

|
All Internet traffic travels between two points addressed by their numeric IP address. An IP address consists of four octets (and 8 bit binary number) which we write in decimal and with dots to separate the octets, e.g. 169.212.123.21. Every web server has a corresponding IP address like that.
To make the Internet more friendly, we are more used to using names rather than numbers (e.g. www.draytek.co.uk) but those names still need to be converted back into their real numeric address for the data to be sent; this is known as 'name resolution;. For example, www.draytek.co.uk might 'resolve' to IP address 212.227.119.69.
A 'DNS server' does this conversion for us - it provides the lookup service for names to IP addresses, so all PCs need to know of a DNS server in order to resolve addresses.
If your PC is gettings its own IP address automatically from the router (using 'DHCP'), then it will also be told of the DNS server to use. The router will use pre-set DNS servers initially, but once it has connected to the ISP, the ISP will allocate their own DNS servers which are then used by the router.
The Vigor routers provide a DNS proxy facility by default. This means that instead of the client PCs on your LAN being told the IP address of the real DNS server, they are told to use the router's own IP address for DNS lookups - the router then responds to these DNS lookups by communicating with the real DNS server. The router maintains a cache so that repeated lookups of the same address don't required repeated DNS Server requests. PCs also maintain their own DNS cache. You can see the router's current DNS Server addresses on the Online Status screen. You can view a WindowsXP PC's current DNS Server settings from the command prompt:
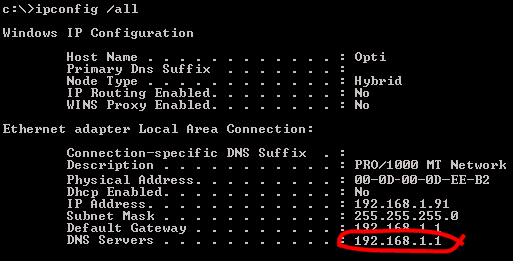
Alternatively, you can over-ride all DNS server settings and force your own by entering them into the DNS fields on the LAN setup menu :
By default, if your ISP allocates its own DNS servers when the router logs into the ISP, these will then over-ride the manual settings. If you want to force the manual settings to apply, from telnet you can use this command:
srv dhcp frcdnsmanl on (use 'off' to disable it. Requires f/w 2.5 or later).
In more recent firmware (September 05 onwards, varies with model) a new command has been added which supercedes the above command:
vigor> ip dns a.a.a.a b.b.b.b
a.a.a.a and b.b.b.b are optional manually entered DNS addresses, and equivalent to entering them into the router's WUI. The router will determine the DNS server addresses in the following priority (highest first):
NOTICE : This document is © SEG Communications and may not be distributed without specific written consent. Information and products subject to change at any time without notice.