
General Router FAQ
Using MultiNAT

|
General Router FAQUsing MultiNAT |

|
In the most common type of router installation, the user uses the NAT facility of the router. NAT, Network Address Translation creates a many-to-one relationship from your private IP addresses to your single public IP address. This means that regardless of your internal private IP address, you appear on the Internet as your single public IP address (static or dynamic). This provides inherrent security to your network clients because their private address is 'hidden' from the outside world and normally cannot be reached directly, unless it solicits contact, or you deliberately open up ports/protocols to it.
Multi-NAT can be used where you have been allocated multiple public IP addresses by your ISP. Instead of a many-to-one relationship, you can have a one-to-one relationship between a public IP address and an internal/private IP address. This means that you have have the protection of NAT (see earlier) but the PC can be addressed directly from the outside world by its aliased public IP address, but still by only opening specific ports to it (for example TCP port 80 for an http/web server).

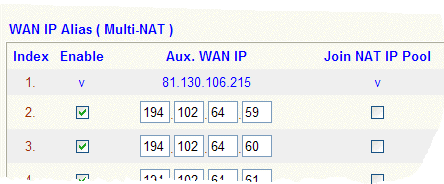
Once you have entered some of your public IP addresses into the MultiNAT/IP Alias menu (reached from the Internet Access / PPPoA setup page - as above), those addresses will then be selectable on either the NAT/Open Ports menu or the NAT / DMZ menu.
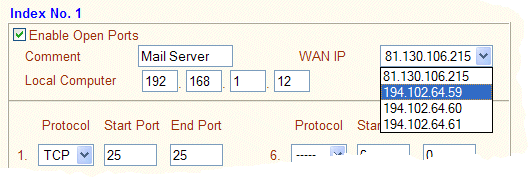

For outgoing traffic which isn't a reply to an incoming server request, outgoing packets from the internal clients will take the router's primary WAN IP address as their source IP address. If you enable the setting of 'Join IP Pool' then the client will appear on any of the multi-NAT addresses.
Problems Accessing Secure sites (e.g. banking): After enabling MiultiNAT, if LAN users have problems with banking or other high security sites, you should uncheck "Join NAT IP Pool" (as shwon in the image above). Having that box enabled randomises the outgoing IP address from the pool.
In a typical MultiNAT scenario, a specific WAN IP address will map to a specific internal LAN (private) IP address for incoming traffic. That is useful for hosting services on specific ports whilst retaining default firewalling facility of the router on other ports. There are circumstances where you might want to expose an internal PC and that any sessions it instigates to the WAN have a source IP address fixed from your IP Pool. This will happen automatically when you use the DMZ facility on a MultiNAT address.
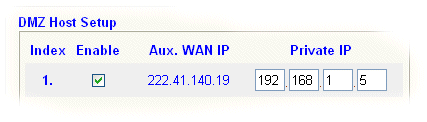
In the above example, therefore, when PC 192.168.1.8 sends anything to the Internet, it will have a source IP address of 222.41.140.19
NOTICE : This document is © SEG Communications and may not be distributed without specific written consent. Information and products subject to change at any time without notice.